Top 10 Circuit Boards: Key Features, Uses, and Buying Guide for Enthusiasts
In the realm of electronics, circuit boards stand as the backbone of modern technology, enabling the complex functionality of various devices we encounter daily. From everyday household gadgets to sophisticated computing systems, circuit boards play a crucial role in connecting components and facilitating their coordinated operations. This introduction provides a gateway for enthusiasts looking to explore the vital features, applications, and practical considerations when purchasing circuit boards, ensuring they make informed decisions for their projects.
As the technology landscape continues to evolve, understanding the different types of circuit boards available becomes paramount for hobbyists and professionals alike. The versatility of these boards allows for endless customization, whether for building a simple electronic project or developing intricate systems. This guide delves into the essential attributes of the top circuit boards on the market, highlights their primary uses, and offers a comprehensive buying guide tailored for enthusiasts ready to dive into the exciting world of electronics. Knowing what to look for in circuit boards can empower creators to not only enhance their skills but also to innovate and bring their ideas to life.

Top 10 Circuit Boards: An Overview of Essential Features
When it comes to selecting the right circuit board for your project, understanding the essential features is crucial. Circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronics, with applications ranging from simple gadgets to complex industrial machinery. Key features include the board's material composition, layer count, thickness, and surface finish. According to industry reports, the market for printed circuit boards (PCBs) is projected to reach $83 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing importance of quality in electronic design.
One of the most critical aspects of circuit boards is their substrate material, which affects both performance and durability. Common materials like FR-4 and aluminum offer different benefits; for instance, FR-4 is favored for its electrical insulation properties, while aluminum may provide better thermal dissipation. Additionally, the layout of the circuit board must be meticulously designed to optimize signal integrity, especially in high-speed applications where signal loss can significantly impact performance.
Tips: When choosing a circuit board, always consider the specific requirements of your project. For example, if your design involves high frequencies, using a board with low-loss dielectric materials can enhance performance. Furthermore, consulting with manufacturers about custom designs can save you from common pitfalls associated with off-the-shelf solutions, ensuring that your circuit board meets your exact needs.
Top 10 Circuit Boards: Key Features Comparison
Understanding Different Types of Circuit Boards and Their Applications
Circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronic devices, playing a crucial role in the connectivity and functionality of various applications. Understanding the different types of circuit boards is essential for enthusiasts to select the right kind for their projects. The most common types include printed circuit boards (PCBs), flexible circuit boards, and rigid-flex boards, each serving distinct purposes. According to industry reports, the global PCB market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics and automotive applications.
Printed circuit boards are widely used in consumer electronics, computers, and telecommunications, known for their reliability and extensive design options. Flexible circuit boards, on the other hand, offer greater versatility and are often found in wearable technology and medical devices where space is limited. Rigid-flex boards combine the benefits of both types, providing flexibility in design while maintaining robust performance in compact spaces. A study by Research and Markets indicates that the flexible PCB segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% through 2025, reflecting a surge in applications across various industries.
In addition to design and application differences, enthusiasts should also consider factors such as material composition, layer count, and manufacturing capabilities. High-frequency materials, for example, are essential for communications equipment, while multi-layer boards are preferred for complex devices requiring efficient space utilization. With the industry continuously evolving, staying updated on these features will empower enthusiasts to make informed choices for their projects.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying Circuit Boards for Your Projects
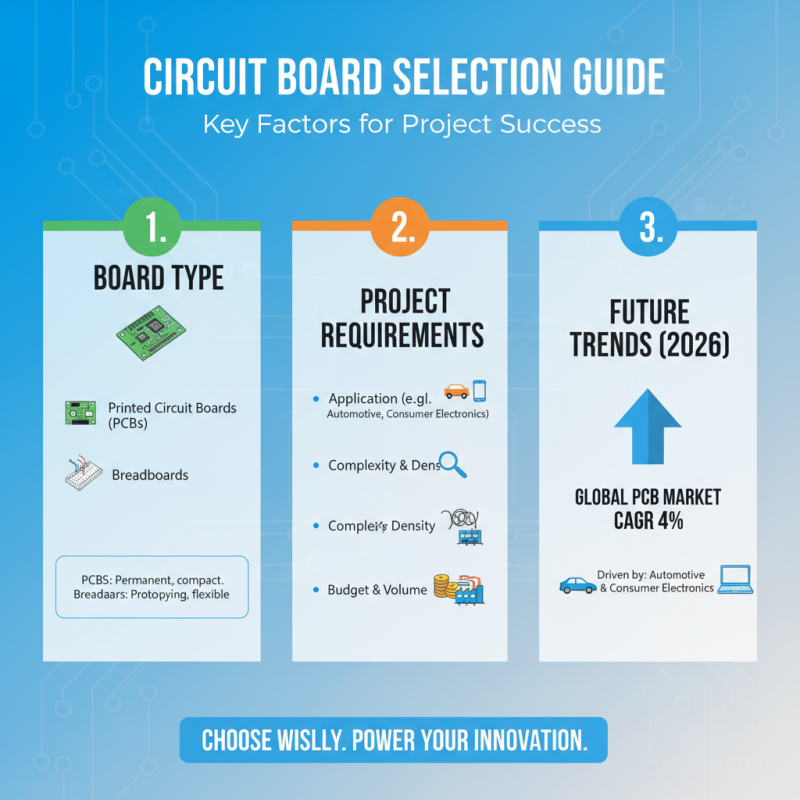
When embarking on a project that involves circuit boards, understanding the key factors to consider can significantly enhance the outcomes of your work. One of the primary aspects is the type of circuit board you need, such as printed circuit boards (PCBs) or breadboards. According to a recent industry report, the global PCB market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4% through 2026, driven by the increasing demand in sectors such as automotive and consumer electronics. This growth underscores the importance of selecting the right type of circuit board tailored to your project's specific requirements.
Another crucial factor to consider is the specifications of the circuit board, including the material composition, layer count, and thickness. PCBs are typically made from materials like FR-4, which offers a good balance between durability and cost-effectiveness. Research indicates that a multi-layer PCB can accommodate more complex circuits, making them essential for advanced applications. Furthermore, understanding the intended application—whether it’s for low-power devices or high-frequency communications—will guide you in selecting a board that meets electrical and thermal management needs. By aligning your choices with project goals and industry standards, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability in your electronic designs.
Comparing Popular Circuit Board Brands and Their Unique Offerings
When delving into the world of circuit boards, enthusiasts often encounter a diverse array of brands, each offering unique features and capabilities. From custom designs to off-the-shelf solutions, the market is saturated with options that cater to various applications, from consumer electronics to automotive systems. According to industry reports, the global circuit board market is projected to reach approximately $75 billion by 2025, reflecting a growing demand driven by advancements in technology and increased electronic device consumption.
Key comparisons among popular circuit board brands often focus on their material composition, layer count, manufacturing capabilities, and specialized features. For instance, some manufacturers excel in producing high-frequency PCBs suited for telecommunications, while others may focus on flexible circuit boards for wearable technology. Enthusiasts should consider these factors carefully, as they directly influence performance, durability, and overall project success.
Tips for choosing the right circuit board:
- Assess the specific requirements of your project. Different applications may necessitate unique specifications, such as higher thermal resistance or compatibility with particular frequencies.
- Look for manufacturers with robust quality control measures. This can significantly reduce the risk of defects and ensure consistent performance throughout the lifecycle of the circuit board.
- Consider the availability of technical support and resources provided by the brand. A knowledgeable support team can prove invaluable for troubleshooting and maximizing the functionality of your circuit boards.
Tips for Maintaining and Troubleshooting Circuit Boards Effectively
Maintaining and troubleshooting circuit boards can seem daunting, but with the right approach, enthusiasts can effectively handle common issues. One of the first steps in maintenance is to regularly inspect the board for signs of wear, such as corrosion or burnt traces. Keeping the board clean from dust and debris can prevent electrical shorts and ensure optimal performance. Using a soft brush and isopropyl alcohol can safely remove any contaminants, and it’s advisable to avoid using excessive force, which could damage delicate components.
When it comes to troubleshooting, a systematic approach is crucial. Start by checking the power supply to ensure that the board is receiving adequate voltage. Use a multimeter to test connections and identify any dead components. If symptoms persist, desoldering components for individual testing can reveal issues. Moreover, referencing schematics can aid in pinpointing fault areas. Cultivating a habit of documenting changes and repairs is beneficial, as this not only helps in tracking the history of the circuit board but also assists in identifying recurring problems.
With patience and steady hands, enthusiasts can master the art of maintaining and troubleshooting circuit boards effectively.
Related Posts
-
The Future of Printed Circuit Boards: Innovations Shaping Our Electronic Devices
-
Top 10 Tips for Efficient Circuit Board Manufacturing Process Optimization
-
2025 Top 5 Trends in Circuit Board Design You Can't Afford to Miss
-

10 Best Circuit Board Design Tools for Efficient Electronics Development
-
Top 5 Essential Features of High Quality PCB Boards for Your Projects
-
How to Get Quick Turn PCB Prototyping for Your Project Needs
