10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Production?
In the ever-evolving landscape of PCB production, mastering key techniques is crucial for success. According to a report from IPC, the global PCB market is expected to reach $70 billion by 2026, highlighting the industry's immense growth potential. Expert Dr. Emily Chen emphasizes, "Successful PCB production hinges on attention to detail and constant innovation."
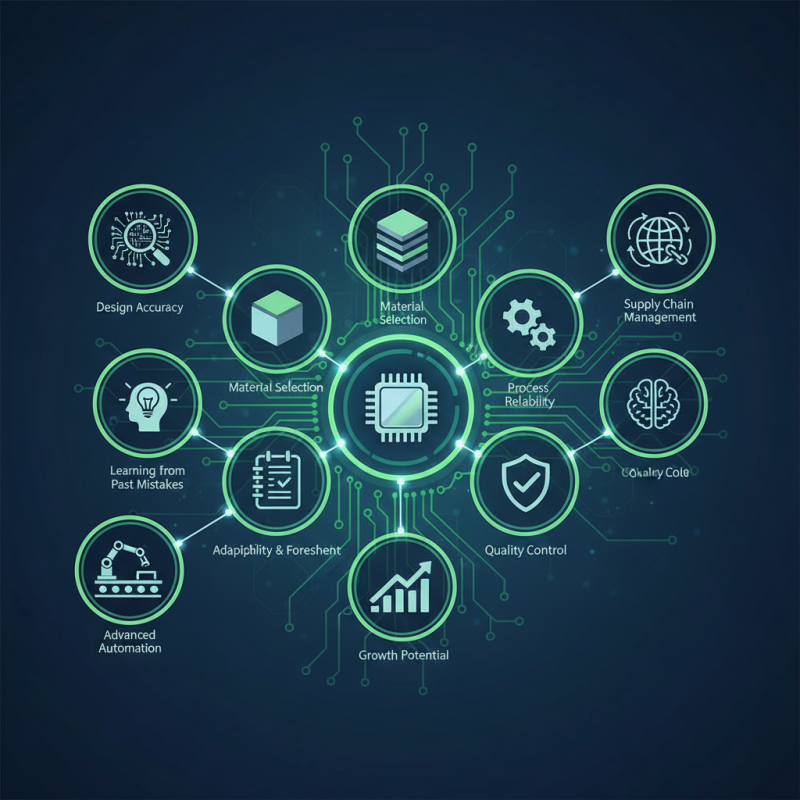
Navigating challenges in PCB production requires more than just technical skills. Factors such as material selection, design accuracy, and process reliability play significant roles. Recent surveys suggest that nearly 35% of manufacturers face issues related to supply chain delays. This underscores the need for adaptability and foresight in production planning, as well as the willingness to learn from past mistakes.
Investing in the right technology is vital. Implementing advanced automation can improve efficiency but may require a steep learning curve. Additionally, quality control processes often need refining, as a single error could compromise an entire batch of PCBs. The path to successful PCB production is fraught with obstacles, yet each misstep offers valuable insights for future projects.

Understanding PCB Design Fundamentals
Understanding PCB design fundamentals is crucial for successful production. Every successful PCB is rooted in a well-thought-out design process. According to industry reports, poor design can account for nearly 30% of production failures. This highlights the importance of meticulous planning and attention to detail during the design phase.
Layer stack-up is one key aspect. Each layer in a PCB serves specific functions, such as grounding or signal integrity. Improper layer configuration can lead to electromagnetic interference, increasing production costs. Designs should also account for thermal dissipation. Inadequate thermal management is a common oversight that can shorten a PCB's lifespan.
A recent study found that designs with poor thermal considerations can lead to a 15% failure rate in high-power applications. Material selection is another critical factor. Choosing the wrong substrate material can negatively impact the performance and reliability of a PCB.
For instance, FR-4 is widely used but may not be suitable for high-frequency applications. Designers must understand the trade-offs. Cost-saving choices can lead to significant performance issues. Reviewing industry standards and data, like IPC-2221, can guide better decisions. Design flaws often arise from a lack of understanding, leading to increased revision cycles and ultimately impacting project timelines.
Choosing the Right Materials for PCB Production
Choosing the right materials for PCB production is crucial. Different applications demand various properties. For example, high-frequency circuits need materials that handle signal integrity well. According to industry reports, FR-4 is still the most common choice for PCBs. However, specialized applications might require advanced materials like Rogers or Taconic.
Cost plays a significant role in material selection. A study noted that nearly 30% of PCB production costs come from materials. Choosing cheaper materials might save money upfront but can lead to performance issues later. It's essential to consider long-term reliability. Printed circuit boards often face thermal stress and environmental factors. Therefore, ensuring the chosen materials can withstand these conditions is vital.
Errors in material selection can lead to significant delays. Approximately 15% of PCB production defects arise from inappropriate material choices. This can reflect poorly on the entire production process. Engineers should focus on material properties such as thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and tensile strength. Often, the right choice is not the most obvious one. Balancing cost, performance, and reliability is not easy, but it is necessary for successful PCB production.
Essential Manufacturing Processes in PCB Fabrication
In the world of PCB fabrication, certain processes are crucial for achieving high-quality results. Understanding these essential manufacturing stages can significantly impact overall production efficiency. Begin with designing a robust PCB layout. Utilize software tools that allow simulation to detect potential issues early. This proactive approach saves time and resources.
Pick the right materials for your PCB. The substrate choice matters. Different materials affect thermal and electrical performance. Ensure your selection aligns with the project's requirements. Many forget to adjust for environmental factors, which can lead to failures later.
Tip: Always test prototypes before mass production. This step identifies design flaws and manufacturing inconsistencies. It’s a learning opportunity. Use feedback to refine the design. Pay attention to the soldering process. Poor solder joints can lead to circuit failures. Quality checks at this stage are vital. Not paying enough attention here may cause significant setbacks.
10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Production
| Tip Number | Tip | Description | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Design for Manufacturability | Ensure PCB design is optimized for production capabilities. | High |
| 2 | Choose the Right Materials | Select suitable substrates and components based on application needs. | Medium |
| 3 | Run Prototype Tests | Test prototypes to identify flaws before mass production. | High |
| 4 | Optimize Manufacturing Processes | Streamline processes to reduce costs and time. | Medium |
| 5 | Implement Quality Control | Establish rigorous inspection protocols during production. | High |
| 6 | Utilize Advanced Technology | Incorporate cutting-edge technology in manufacturing equipment. | Medium |
| 7 | Collaborate with Suppliers | Engage with suppliers for better materials and components. | High |
| 8 | Review Regulatory Compliance | Ensure PCBs meet relevant industry standards and regulations. | High |
| 9 | Plan for Scaling Up | Prepare production strategy for potential scale-up. | Medium |
| 10 | Continuously Improve | Regularly analyze production processes for improvements. | High |
Quality Control Measures in PCB Production
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of PCB production. A recent industry report highlights that about 30% of PCBs face issues due to inadequate QC measures. These problems often lead to costly rework and delayed production schedules. Investing in robust QC protocols can significantly reduce failures and enhance reliability. For example, implementing automated optical inspection (AOI) can catch defects early. This technology can increase defect detection rates by nearly 90%.
In addition to technological advancements, training staff is essential. Continuous education ensures that workers understand the latest QC practices. An industry survey indicates that employee training can reduce error rates by up to 50%. Workers need to grasp the importance of meticulous work. Even minor mistakes can lead to significant challenges in PCB performance. Furthermore, conducting regular audits of the production process helps maintain standards. This practice highlights gaps in QC that need addressing over time.
Despite advances, some issues still slip through the cracks. Human error remains a real concern. For instance, problems with soldering can lead to intermittent connections. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of production can help mitigate such risks. Evaluating past mistakes makes it easier to improve practices. It is essential to reflect on both successes and failures in the PCB production journey.
10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Production
Tips for Efficient PCB Assembly and Testing

Efficient PCB assembly and testing are crucial for successful production. Start by ensuring that the components are clean and properly oriented. A chaotic workspace can lead to errors. Implementing a well-organized workflow saves time and enhances accuracy. Using a designated area for tools and components helps maintain focus.
Testing should begin early in the assembly process. This prevents cumulative errors, which can be costly later on. However, many overlook this step. A simple test after placing each component can identify issues. It’s also helpful to automate testing where possible. Automation can streamline processes and reduce human error.
Reviewing the assembly and testing processes is vital for improvement. Gather feedback from team members. Reflect on what went right and what didn’t. Mistakes are inevitable, but analyzing them fosters growth. Understanding each step’s impact on the final product is essential.
Related Posts
-
Unlocking Efficiency: The Future of PCB Production Techniques in Modern Electronics
-

10 Best Tips for Effective PCB Printing Techniques and Processes
-
Transforming Industries: The Future of PCB Production and Its Impact on Technology
-
How to Choose the Right PCB Fabrication Process for Your Project Needs
-
Innovative Trends in PCB Printing That Will Transform the Electronics Industry
-

What is PCB Board Design? A Complete Guide for Beginners and Pros
