10 Best PCB Board Options for Your Electronics Projects?
When embarking on your electronics projects, selecting the right pcb board is crucial. The right board can enhance functionality and simplify your design process. With countless options available, it can be overwhelming. Understanding the specific requirements of your project is essential.
Different projects may demand various features from a pcb board. Some boards support high-frequency signals, while others excel in low-power applications. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses. The challenge lies in matching a pcb board's attributes to your project’s needs.
Consider factors like size, layer count, and material. These can significantly affect performance. Choosing hastily may lead to issues later. Reflecting on your project’s long-term goals can guide your decision. The right pcb board choice can be a game changer for your electronics journey.

Understanding PCB Types: A Guide to Common Options
When selecting a PCB for electronics projects, understanding the different types is crucial. PCBs, or printed circuit boards, can vary significantly in materials and design. For instance, FR-4 is the most common type. It consists of fiberglass and epoxy resin. Reports indicate that around 80% of PCBs use FR-4 due to its durability and moisture resistance.
Another option is flexible PCBs. They offer a unique advantage. These boards can bend and fit into compact spaces. Recent industry findings show that the flexible PCB market is expanding at a CAGR of 10% annually. This trend highlights the growing need for space-efficient designs. However, flexible PCBs often come with a higher price tag.
Rigid-flex PCBs also deserve attention. They combine rigid and flexible sections. This design maximizes functionality while minimizing space. They are ideal for complex devices like smartphones. Yet, their production can be challenging, leading to potential quality issues. Balancing performance and cost remains a dilemma for many engineers. Choosing the right PCB is often a complex decision. An informed choice minimizes risk and enhances project success.
10 Best PCB Board Options for Your Electronics Projects
| PCB Type | Material | Layer Count | Thickness (mm) | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided PCB | FR-4 | 1 | 1.6 | Simple electronic devices |
| Double-Sided PCB | FR-4 | 2 | 1.6 | Medium complexity circuits |
| Multilayer PCB | FR-4 | 4+ | 1.6 | High-density applications |
| Rigid PCB | FR-4 | Varies | 1.6 | Consumer electronics |
| Flexible PCB | Polyimide | 1 | 0.2-0.5 | Wearable devices |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | FR-4 / Polyimide | 1+ | Varies | Compact electronics |
| Aluminum PCB | Aluminum | 1 | 1.6 | LED applications |
| High-Frequency PCB | PTFE | 1+ | Varies | RF applications |
| Embedded PCB | FR-4 | 1+ | 1.6 | Advanced electronics |
Factors to Consider When Choosing PCB Boards for Projects
When choosing PCB boards for your electronics projects, several factors are key. Material type can greatly affect performance. Common options include FR-4 and aluminum, each with specific uses. Consider the board thickness and how it relates to your project’s needs. Thicker boards can support heavier components, while thinner boards are beneficial for compact designs.
Think about the manufacturing process as well. Different fabrication techniques impact the final product’s quality and cost. You may need to balance complexity and budget. More layers often mean higher costs but can offer better performance for complex designs. It's important to understand your project's scope and future needs.
Tip: Always prototype before finalizing designs. Testing with multiple designs can reveal unforeseen issues. Additionally, consult with engineers if possible. Their insights can help you avoid common pitfalls. Another tip: never compromise on quality. It may be tempting to choose cheaper materials. However, this can lead to failures down the line. Be mindful of this when making your decisions.
Top 10 PCB Board Options: Features and Benefits
When choosing the right PCB board, consider key features that match your project's needs. The materials used can significantly affect performance. For instance, FR-4 is popular for its durability and insulation properties. However, it may not always be the best choice for every application. Some projects require high-frequency performance where specialized materials shine.
Another factor to explore is the size and layer count. A simple design might need a two-layer board. Yet, complex projects could benefit from multi-layer options. More layers allow for increased routing density. But this can also make manufacturing trickier and pricier. Sometimes, a smaller board can lead to unexpected challenges during assembly.
Don't overlook the importance of the surface finish. Different finishes provide varying levels of protection and solderability. A finish that works well in one context might cause problems in another. Evaluate your project's environment carefully. Every element can make a difference. Experimenting with these options can lead to better performance. Yet, it also requires careful planning and testing. Understand the trade-offs involved in each choice you make.
Comparative Analysis: Rigid vs. Flexible PCBs
Rigid and flexible PCBs serve different purposes in electronics projects. Rigid PCBs offer sturdiness. They are ideal for devices that require a stable platform. Think of traditional circuit boards in computers. They excel in signal integrity due to their fixed structure. However, this rigidity can limit design flexibility.
On the other hand, flexible PCBs are quite adaptable. They bend and twist easily, making them perfect for wearable technology. Imagine a fitness tracker that conforms to your wrist. This flexibility allows for innovative designs but can pose challenges. They are often more delicate and can be prone to wear over time. A poorly-manufactured flexible PCB might fail under stress. Designers must carefully consider material choices and thickness to avoid issues. Balancing these aspects is crucial for project success.
Comparative Analysis of Rigid vs. Flexible PCBs for Electronics Projects
Cost-Effective Solutions: Budget-Friendly PCB Choices
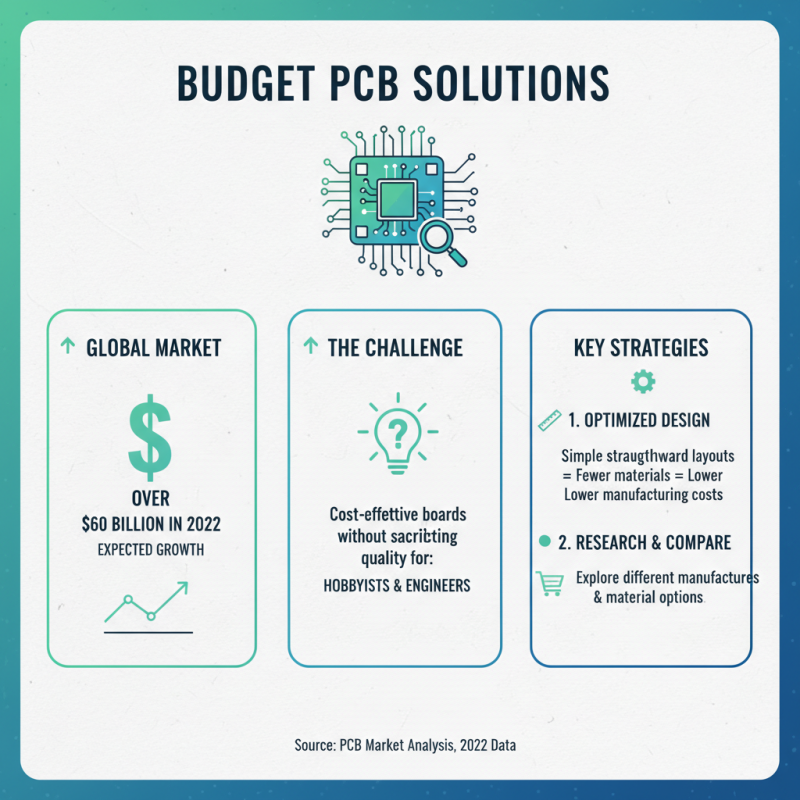
When it comes to electronics projects, finding budget-friendly PCB board options can be a challenge. The global PCB market was valued at over $60 billion in 2022, with significant growth expected. Many hobbyists and engineers seek cost-effective solutions without sacrificing quality. A well-structured design can save costs significantly. Research shows that more straightforward layouts require fewer materials and can lead to lower manufacturing prices.
Affordable PCB options often utilize standard materials. FR-4 is a popular choice, providing decent electrical performance at a low cost. Reports indicate that using a well-optimized design can reduce production costs by up to 30%. Complex circuits may require more expensive substrates. In contrast, simpler designs can be effective and budget-friendly. Before choosing, carefully consider the project requirements and potential limitations.
Prototyping is another area where costs can spiral. Rush orders typically add expense. It’s essential to factor in lead times and design revisions. An iteration might seem inefficient, but it leads to better results in the long run. While there are many budget options, each decision impacts the final outcome. Balancing cost and performance demands clear prioritization. Reflecting on priorities may reveal alternative routes that meet both quality and budget expectations.
Related Posts
-
Transforming Industries: The Future of PCB Production and Its Impact on Technology
-
How to Choose the Right PCB Fabrication Process for Your Project Needs
-

10 Best Tips for Effective PCB Printing Techniques and Processes
-

10 Essential Tips for Successful PCB Production?
-
Top 5 Essential Features of High Quality PCB Boards for Your Projects
-
Unlocking Efficiency: The Future of PCB Production Techniques in Modern Electronics
